The esims.AI Blog: Giving you the lowdown on all things Travel eSIM
eSIM Adoption Hits Inflection Point, Poised for Hyper-Growth
Published on by Sabrina in News. Last updated on .
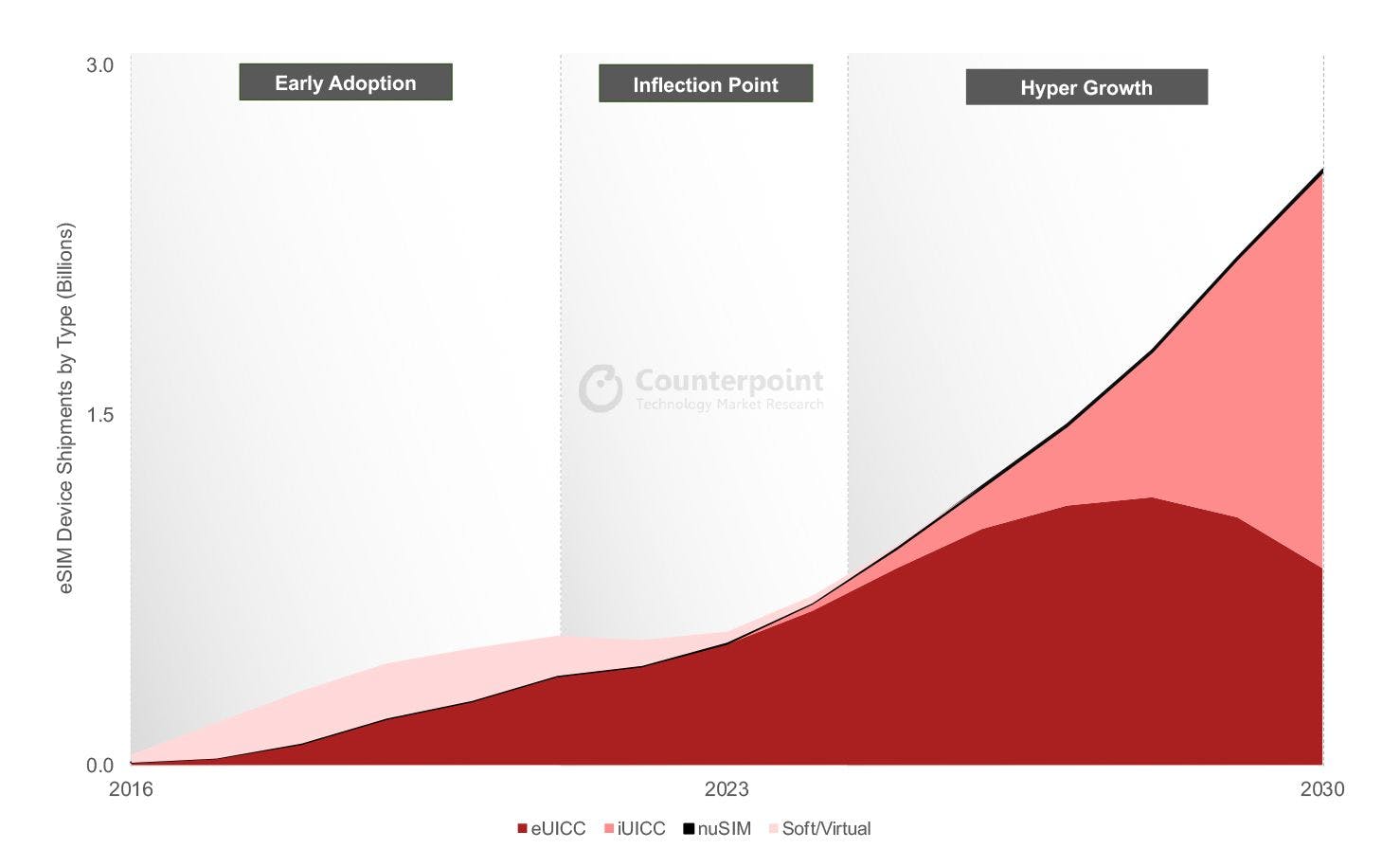
Based on a new report from Counterpoint Research, eSIM adoption has reached an inflection point and is entering a high-growth phase. More than 6 billion devices with embedded or integrated SIM cards, collectively referred to as xSIM (eSIM + iSIM) devices, are expected to be shipped over the next five years.
An embedded SIM card, or eSIM, is pre-installed in a device and can't be physically swapped, instead, it's programmed remotely and can hold several SIMs at once. An integrated SIM (iSIM) is integrated into a device's main processor, eliminating the need for dedicated hardware.
The adoption of eSIMs is growing across the smartphone, IoT, and automotive markets, driving a 11% year-over-year growth in eSIM device shipments in 2022, reaching 424 million units, despite a 3% overall drop in cellular-connected device shipments, according to the report.
By 2030, it's projected that 70% of all cellular devices will support eSIM technology. This includes 100% adoption in the smartwatch and drone segments; 92% for connected cars; 82% for smartphones; and 79% for tablets. Smartphones will continue to be the primary driving category, accounting for more than 40% of all eSIM devices.

The physical MFF2/WLCSP form-factor soldered eSIM chip has been the dominant standard for eSIM implementation. Over the next five years, hardware-based eSIM is expected to remain dominant, accounting for over half of all shipments. However, the first wave of mainstream iSIM adoption will be seen across IoT applications. Beyond 2028, iSIM is projected to become the dominant SIM form factor, with the shipments of iSIM-capable devices climbing to a cumulative 4 billion units by 2030. This will mean a more seamless connectivity experience for customers looking to purchase travel data connectivity options, such as the remote provisioning of SIM profiles to your device.
Smartphones have played a key role in driving primary eSIM awareness among consumers and mobile network operators (MNOs), although awareness is still in its infancy. The growing cellular connectivity in smartwatches has helped increase the penetration of eSIM-supported smartwatches. Other cellular-capable consumer devices such as laptops and tablets will also see rapid eSIM adoption in the coming years.
Emerging device categories such as XR and drones will be the fastest-growing categories. 5G-connected drones that will benefit from eSIM technology and drive adoption across several use cases like last-mile delivery, disaster management, search and rescue, education, construction, and agriculture. Connected cars are one of the largest and most obvious use cases for eSIMs. Consistent connectivity experience for mobility applications is becoming paramount, particularly for safety use cases such as eCall and the future rise of autonomous driving.
This increased adoption of eSIM is driven by greater awareness among MNOs and device manufacturers, facilitated by the flexibility, cost efficiency, security, cost savings, and the key role eSIM is playing in the digital transformation of Mobile Network Operators.
This can only be good news for consumers looking for more choice, and will open up a new paradigm of connectivity options in a global world.